图片懒加载
入口文件
html
// index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>LazyLoad</title>
<style>
.block {
height: 100vh;
width: 50vw;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="block"></div>
<img width="500" height="500" data-src="https://s2.loli.net/2023/03/20/KyI7GqbewhplP6O.png" />
<img width="500" height="500" data-src="https://s2.loli.net/2023/05/02/DFgoUH1qcrBYsLC.png" />
<img width="500" height="500" data-src="https://s2.loli.net/2023/04/26/pOPWherMAK5XaHz.png" />
</body>
</html>实现方法:
首页,需要为每个
img标签添加data-src属性,并且不能添加src属性(即使src=""也不允许, 除非有专门的loading.gif资源)。window.InnerHeight+document.documentElement.scrollTop-item.offsetTop> 0.png)
jsconst imgs = Array.from(document.querySelectorAll('img')); const loadPic1 = () => { imgs.forEach((item) => { if(document.documentElement.scrollTop + window.innerHeight - item.offsetTop > 0) { item.src = item.dataset.src; } }); }item.getBoundingClientRect().top<window.innerHeight.png)
jsconst loadPic2 = () => { imgs.forEach((item) => { if(item.getBoundingClientRect().top <= window.innerHeight) { item.src = item.dataset.src; } }); }添加
scroll事件html// index.html // ... <body> // ... <script src="./lazyload.js"></script> <script> loadPic1(); // 首次进入页面的时候,对一开始就满足加载条件的图片加载一次 window.addEventListener('scroll', loadPic1); // loadPic2(); // window.addEventListener('scroll', loadPic2); </script> </body>warning😶
在当前情况下,滚动事件每次滚动都会重复触发,滚动一次可能就触发几十上百次的事件。
解决方案:通过
节流throttle对loadPic进行处理,可以避免多次触发事件。节流方法的实现可以参考防抖与节流html<script src="../防抖与节流/throttle.js"></script> <script> loadPic1(); window.addEventListener('scroll', throttle(loadPic1,0.5)); // ... </script>并且,当重复滚到同一图片位置的时候,即使图片已经加载成功,同样会重新发送请求获取图片。
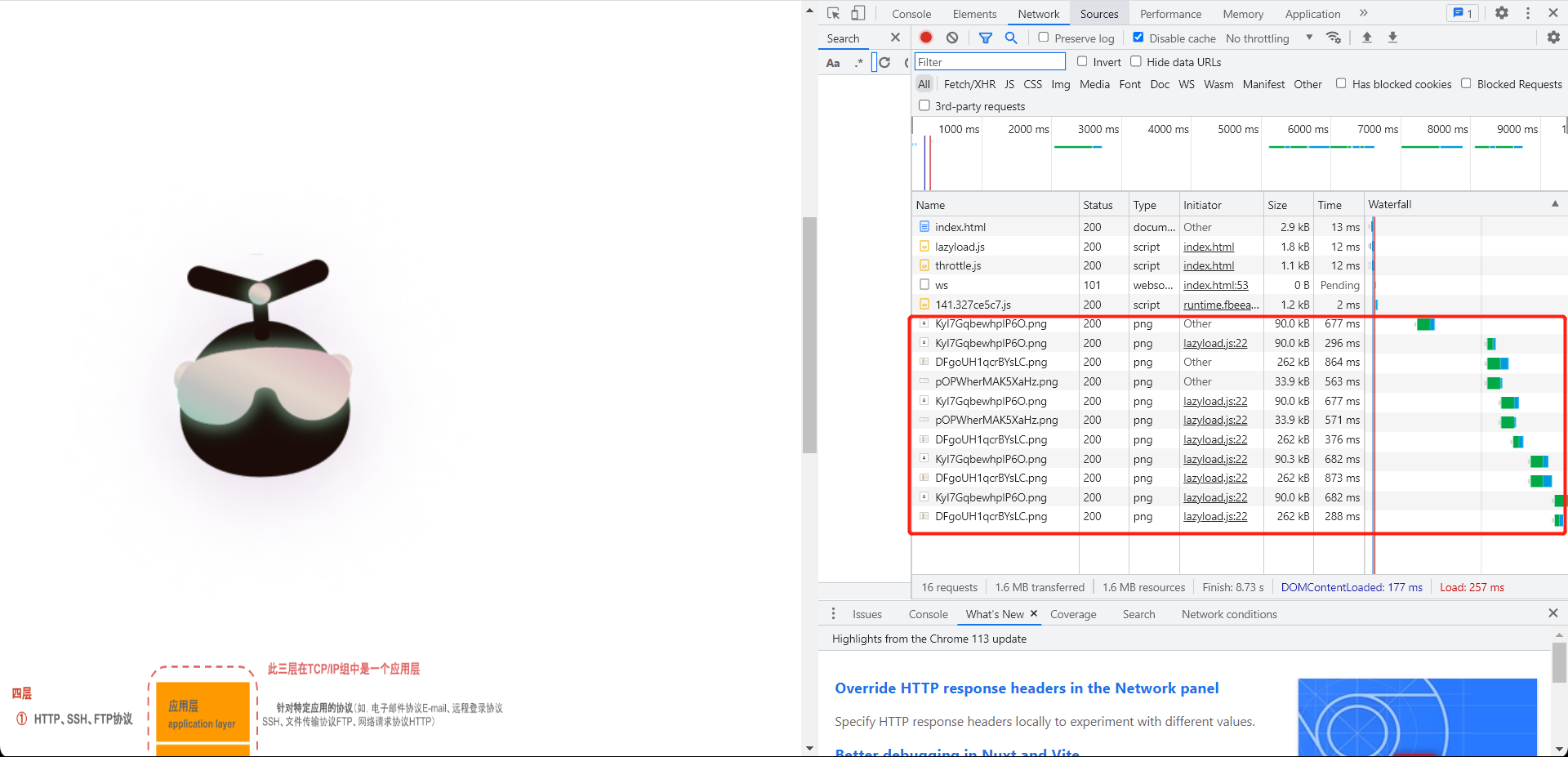
解决方案:当加载图片后不替换
src为dataset.srcjs// lazyload.js // ... const loadPic1 = () => { if(item.src) return; // 如果item有src属性说明图片已经被加载,之所以上面说到src=""也不允许,这是因为src=""的时候,item.src也是有值的,值为当前的html的地址,当然如果使用loading图片的话,设置为item.src !== 'loading的url'即可 // ... }
IntersectionObserver优势🎇
使用
IntersectionObserver相对于使用scrollTop和getBoundingClientRect方法来实现懒加载具有以下优势:- 更高效的触发:
IntersectionObserver提供了一种更高效的触发方式,它可以在目标元素进入或离开视窗可见区域时立即通知观察者。相比之下,使用scrollTop和getBoundingClientRect方法需要监听滚动事件或定时轮询来检测元素的位置变化,这可能会导致性能问题。 - 减少资源消耗:使用
IntersectionObserver可以有效减少不必要的计算和处理。它只关注目标元素与视窗的交叉状态,并在交叉状态发生变化时触发回调函数,而不需要频繁计算元素的位置和滚动距离。 - 更精确的判断:
IntersectionObserver判断目标元素是否进入可视区域时(0 <= intersectionRatio <= 1),考虑了元素的交叉面积,而不仅仅是位置。这使得判断更加准确,避免了一些边界情况和误判。 - 支持懒加载以外的观察行为:
IntersectionObserver不仅可以用于懒加载,还可以观察其他类型的交叉行为,比如监听元素与容器的交叉、元素与其他元素的交叉等。这使得它具有更广泛的应用场景。
总的来说,使用
IntersectionObserver可以提供更高效、更准确的懒加载实现,同时也具备更灵活的观察能力,适用于各种交叉观察场景。相比之下,使用scrollTop和getBoundingClientRect方法需要更多的手动计算和处理,容易引入性能问题。jsconst observer = new IntersectionObserver((entries, observer) => { entries.forEach((entry) => { if(entry.intersectionRatio > 0) { // >0说明有视窗交叉 const img = entry.target; img.src = img.dataset.src; observer.unobserve(img); // 加载完毕即取消监听 } }) }) const loadPic3 = () => { imgs.forEach((item) => { observer.observe(item); }) }- 更高效的触发:
代码总结😎
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>LazyLoad</title>
<style>
.block {
height: 100vh;
width: 50vw;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="block"></div>
<img width="500" height="500" data-src="https://s2.loli.net/2023/03/20/KyI7GqbewhplP6O.png" />
<img width="500" height="500" data-src="https://s2.loli.net/2023/05/02/DFgoUH1qcrBYsLC.png" />
<img width="500" height="500" data-src="https://s2.loli.net/2023/04/26/pOPWherMAK5XaHz.png" />
<script src="./lazyload.js"></script>
<script src="../防抖与节流/throttle.js"></script>
<script>
// loadPic1();
// window.addEventListener('scroll', throttle(loadPic1,0.5));
// loadPic2();
// window.addEventListener('scroll', throttle(loadPic2,0.5));
loadPic3();
</script>
</body>
</html>js
console.log('lazyload');
imgs = Array.from(document.querySelectorAll('img'));
const loadPic1 = () => {
imgs.forEach((item) => {
console.log('emit');
// console.log(document.documentElement.scrollTop, window.innerHeight, item.offsetTop);
if(item.src) return; // 如果item有src属性说明图片已经被加载,之所以上面说到src=""也不允许,这是因为src=""的时候,item.src也是有值的,值为当前的html的地址,当然如果使用loading图片的话,设置为item.src !== 'loading的url'即可
if(document.documentElement.scrollTop + window.innerHeight - item.offsetTop > 0) {
item.src = item.dataset.src;
}
});
}
const loadPic2 = () => {
imgs.forEach((item) => {
console.log('emit2');
// console.log(item.getBoundingClientRect().top, window.innerHeight);
if(item.src) return;
if(item.getBoundingClientRect().top <= window.innerHeight) {
item.src = item.dataset.src;
}
});
}
const observer = new IntersectionObserver((entries, observer) => {
entries.forEach((entry) => {
if(entry.intersectionRatio > 0) { // >0说明有视窗交叉
const img = entry.target;
img.src = img.dataset.src;
observer.unobserve(img); // 加载完毕即取消监听
}
})
})
const loadPic3 = () => {
imgs.forEach((item) => {
observer.observe(item);
})
}